By now, someone may have become accustomed to the sum we formed sumtime this Fall:
(1) ![]()
We’ve summoned this sum again in order to study its extremum behaviour, which we found to be somewhat fun. As is the norm, we’ll use the platform of calculus to this end and then give a summary of our findings just after example 10. See you there!!!
Partial fraction decomposition
So we want to obtain the first two derivatives of the rational function (1). By default, the quotient rule should be used, but the fault here is that it gets a bit difficult — especially for the second derivative — and so we’ve chosen a different route.
If the denominator of a rational function is a product of linear factors, it may be suitable in some situations to first split the rational function into its partial fractions before proceeding with differentiation, rather than using the quotient rule. Depending on what one wants, the additional work done may be worth it in the end.
Resolve ![]() into its partial fractions.
into its partial fractions.
The given rational function is improper, so we first put it in a proper form using long division:
![]()
Notice that ![]() . Set
. Set
![]()
and obtain the constants ![]() by the cover-up method:
by the cover-up method:
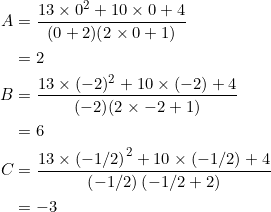
Finally:
![]()
Find the first derivative of ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() .
.
We make use of the partial fraction decomposition from the previous example to compute the derivative (compare this strategy with logarithmic differentiation).
![]()
A breeze.
Find the second derivative of ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() .
.
![]()
Also a breeze because of the underlying work done in the initial partial fraction decomposition. Hard work pays.
Polynomial factoring digression
Factorize ![]() .
.
The presence of some common factors makes the factorization a breeze.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{equation*} \begin{split} &=(r+2)^2(2r+1)^2\Big(r^2-1\Big)-3r^2\Big((2r+1)^2-(r+2)^2\Big)\\ &=(r+2)^2(2r+1)^2\Big(r^2-1\Big)-3r^2\Big(3(r^2-1)\Big)\\ &=(r^2-1)\Big((r+2)^2(2r+1)^2-9r^2\Big)\\ &=(r^2-1)\Big(\left[(r+2)(2r+1)-3r\right]\left[(r+2)(2r+1)+3r\right]\Big)\\ &=(r^2-1)\Big(2r^2+5r+2-3r\Big)\Big(2r^2+5r+2+3r\Big)\\ &=4(r^2-1)(r^2+r+1)(r^2+4r+1) \end{split} \end{equation*}](https://blog.fridaymath.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-55e414ef235ca86c48638ecb8ddc34b8_l3.png)
See that special quadratic ![]() ? Get excited any time you spot it!!!
? Get excited any time you spot it!!!
Find the critical numbers for ![]() .
.
Equate the first derivative to zero and solve for ![]() :
:
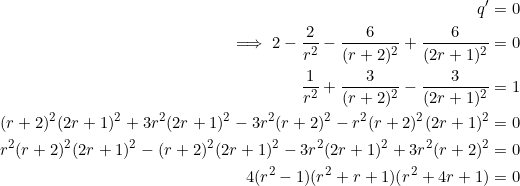
The last line came from the factorization in the preceding example. Equate each factor to zero:
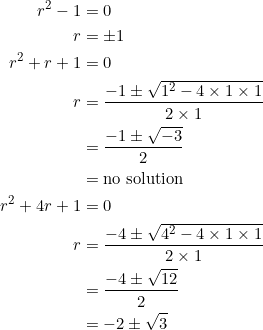
We obtain the critical numbers: ![]() . All stationary/turning points. The vertical asymptotes at
. All stationary/turning points. The vertical asymptotes at ![]() are also critical numbers because the derivative is undefined at each of these, but these values are already exqluded.
are also critical numbers because the derivative is undefined at each of these, but these values are already exqluded.
Pretty familiar deductions
Show that ![]() give local minimum values for
give local minimum values for ![]() .
.
We use the second derivative test.
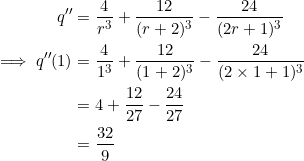
Since the second derivative is positive, ![]() gives a local minimum.
gives a local minimum.
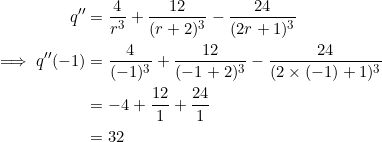
Since the second derivative is positive, ![]() gives a local minimum.
gives a local minimum.
Show that ![]() give local maximum values for
give local maximum values for ![]() .
.
Starting with ![]() , let’s evaluate the second derivative.
, let’s evaluate the second derivative.
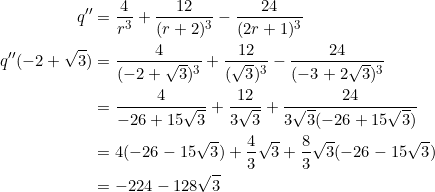
Since the second derivative is negative, we conclude that ![]() gives a local maximum value for
gives a local maximum value for ![]() . Next, we calculate the second derivative when
. Next, we calculate the second derivative when ![]() :
:
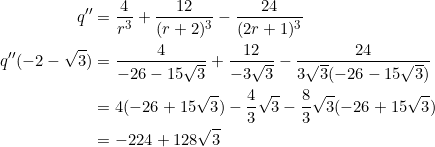
This may require a calculator to ascertain that it’s negative. Indeed, ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() gives a local maximum value for
gives a local maximum value for ![]() .
.
Find the local minimum value(s) and the local maximum value(s) for the rational function ![]() .
.
From the two preceding examples, ![]() give local minimum value(s) while
give local minimum value(s) while ![]() give local maximum value(s). So we compute the corresponding values of
give local maximum value(s). So we compute the corresponding values of ![]() at these points.
at these points.
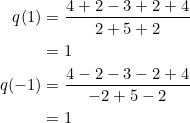
For ![]() , it helps to know that they are both solutions of
, it helps to know that they are both solutions of ![]() . This makes the computation of
. This makes the computation of ![]() easier, and we did that last post:
easier, and we did that last post:
![]()
Thus, the local minimum value is ![]() and the local maximum value is
and the local maximum value is ![]() . (Don’t be surprised that the local minimum value exceeds the local maximum value. They’re local, not global.)
. (Don’t be surprised that the local minimum value exceeds the local maximum value. They’re local, not global.)
Solve the equation ![]() .
.
We suspect that there is no real-valued solution to the given equation. Why? Because the right side exceeds the local maximum value of ![]() (and is smaller than the local minimum value of
(and is smaller than the local minimum value of ![]() ).
).
Let’s confirm our suspicion. Clear fractions to get better traction and continue the solution:
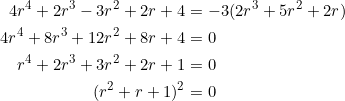
The discriminant of the resulting quadratic is ![]() . Thus, there is no real-valued solution to the quadratic, and hence no real-valued solution to the given rational equation.
. Thus, there is no real-valued solution to the quadratic, and hence no real-valued solution to the given rational equation.
Calqulate ![]() for
for ![]() with vertices at
with vertices at ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
The ingredients we need are the median-slopes:
![]()
and the side-slopes:
![]()
By definition and substitution:
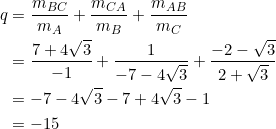
Notice that the given triangle isn’t equilateral, yet satisfies ![]() . In our theory, once a triangle satisfies
. In our theory, once a triangle satisfies ![]() , then it shares some lateral properties with the equilateral triangle.
, then it shares some lateral properties with the equilateral triangle.
(In case you’re wondering how we obtained those coordinates, the building blocks are here in our second post of the year.)
Takeaway
The following statements are equivalent for a triangle with side-slopes ![]() for sides
for sides ![]() :
:




 gives a local maximum value of
gives a local maximum value of 
 or
or  , where
, where  is the common ratio of the median-slopes
is the common ratio of the median-slopes- the common ratio
 is that of an equilateral triangle (or its “look-alike”).
is that of an equilateral triangle (or its “look-alike”).
Okay, qool.
Tasks
- Show that the equation
 has no real-valued solution.
has no real-valued solution. - Solve the equation
 .
. - Given the rational function
 :
:
- Find the discriminant of the quartic numerator
 .
. - Deduce that the graph of the rational function doesn’t cross the
 -axis.
-axis.
- Find the discriminant of the quartic numerator
- Find the interval(s) on which the rational function
 is increasing, and the interval(s) on which it is decreasing.
is increasing, and the interval(s) on which it is decreasing. - Consider the rational function
 . PROVE that:
. PROVE that:
- its partial fraction decomposition is
 .
. - the point
 is a local minimum point.
is a local minimum point. - the point
 is an inflexion point.
is an inflexion point.
- its partial fraction decomposition is
- Consider the rational function
 . PROVE that:
. PROVE that:
- its partial fraction decomposition is
 .
. - the point
 is a local minimum point.
is a local minimum point. - the point
 is an inflexion point.
is an inflexion point.
- its partial fraction decomposition is
- PROVE that the following equations are equivalent:



(These equations play important roles in connection with triangles whose side-slopes form geometric progressions.)
- (Palindromic quartic) Verify that the roots of the quartic
 are:
are: - (Palindromic quartic) Find a monic quartic polynomial whose roots are:
- Show that
 if and only if
if and only if 
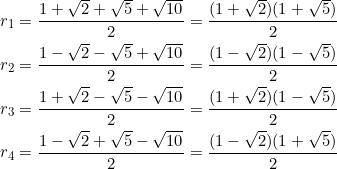
Notice that ![]() and
and ![]() are “multiples” of the golden ratio. Also, it may be more convenient to solve the given quartic, than to substitute the purported roots.
are “multiples” of the golden ratio. Also, it may be more convenient to solve the given quartic, than to substitute the purported roots.
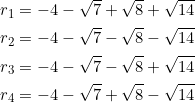
Our sum somehow leads to palindromic polynomials. We may visit this concept in the near posture.